Common Core High School Statistics & Probability Teaching and Learning Resources
Domain: ID: Interpreting Categorical and Quantitative Data
Select the cluster for resources on this page:
ID-A: Summarize, represent, and interpret data on a single count
or measurement variable
ID-B: Summarize, represent, and interpret data on two categorical
and quantitative variables
ID-C: Interpret linear models
ID-A: Summarize, represent, and interpret data on a single count
or measurement variable
Standards:
- ID-A.1. Represent data with plots on the
real number line (dot plots, histograms, and box plots).
- ID-A.2. Use statistics appropriate to the
shape of the data distribution to compare center (median, mean) and
spread (interquartile range, standard deviation) of two or more
different data sets.
- ID-A.3. Interpret differences in shape,
center, and spread in the context of the data sets, accounting for
possible effects of extreme data points (outliers).
- ID-A.4. Use the mean and standard deviation
of a data set to fit it to a normal distribution and to estimate
population percentages. Recognize that there are data sets for which
such a procedure is not appropriate. Use calculators, spreadsheets,
and tables to estimate areas under the normal curve.
Technology-enhanced investigations:
Mathwords.com: Math Dictionary.
Note: Terms followed by * are defined at MathsIsFun.com.
Also see the
Stat
Trek Statistics Dictionary
for terms followed by **. Key vocabulary for this domain. Use with ID-A, ID-B, ID-C:
Academo.org:
Standard Deviation Calculator. After entering the numbers,
this tool shows the number of numbers, the mean, variance, and standard
deviation. A brief explanation of the standard deviation formula
is included. Aligns with ID-A.2 and ID-A.4.
Alcula.com:
BBC GCSE Bitesize Maths, Statistics: Analyzing Data:
Averages: Mean, Mode, and Median --There is an explanation (called
Revise), activity, and test. Also see sections for
Collecting Data and
Representing Data.
Calculator.net: The following also includes explanations of theory
for each calculator
CalculatorSoup:
Descriptive Statistics Calculator. A complete calculator
showing min, max, range, mean, median, mode, standard deviation,
variance, quartiles, interquartiles, outliers, and more. A frequency table is also
shown. Aligns with ID-A.2.
College Preparatory Math: Student Tutorials:
TI-84
Graphing Calculator: Univariate Data: Videos and screen shots
illustrating use of the calculator to set up histograms, box plots,
comparing two box plots, and summarizing data numerically. Use
with ID-A.1.
Imagine Learning Classroom (formerly LearnZillion) subscription
needed:
- Lesson set:
Represent data with dot plots, histograms, and box plots:
Seven video lessons: Create a dot plot, histogram, box plot;
understand the advantages of a dot plot, histogram, box plot;
choose the appropriate graphical representation. Aligns with
ID-A.1.
- Lesson set:
Compare center and spread of two or more data sets: Five
video lessons: Describe data by using measures of center and
spread, distinguish between mean absolute deviation (MAD) and
standard deviation, compare two data sets by using measures of
center and spread, use the appropriate measure of center and
spread when outliers are present or not present. Aligns
with ID-A.2.
- Lesson set:
Compare center and spread of two or more data sets: Seven
video lessons: Identify a data set’s shape using modes and
symmetry, find center using mean and median, calculate and
compare the spread of data sets by identifying the interquartile
range (IQR), calculate and compare the spread of data sets by
finding the standard deviation; compare histograms, box plots,
and dot plots using center and spread. Aligns with ID-A.2.
- Lesson set:
Interpret differences in shape, center, and spread of data sets
in context: Five video lessons: Understand the process of
making inferences; draw inferences from a histogram, by
analyzing data, from data in a box plot, and from data in a dot
plot. Aligns with ID-A.3.
- Lesson set:
Compare center and spread of two or more data sets, accounting
for outliers: Five video lessons: Identify outliers using
knowledge of quartiles, represent outliers in a box plot,
understand the effect of outliers on shape, interpreting
histograms, compare box plots. Aligns with ID-A.3.
- Lesson set:
Use mean and standard deviation to fit a data set to a normal
distribution when appropriate; estimate population percentages
using tools: Six video lessons: Identify situations that fit
a normal distribution, estimate what percentage of a population
falls within a certain range by applying the Empirical Rule,
find population percentages by extending the Empirical Rule,
find z-scores; find population percentages by using z-scores and
tables and by using technology. Aligns with ID-A.4.
- Lesson set:
Use mean and standard deviation to fit to normal distribution
and estimate population percentages when appropriate; use tools
to estimate areas under the normal curve: video lessons:
Check whether normal model is appropriate for a data set,
apply the Empirical Rule to determine if a distribution is
normal, model a data set with a normal probability distribution,
predict intervals and population percentages using the Empirical
Rule, predict population percentages by using a graphing
calculator, solve problems involving the normal distribution by
using a graphing calculator. Aligns with ID-A.4.
MIT BLOSSOMS: Video lesson with additional teacher and learner
resources. Description is from the video summary.
Flaws
of Averages: "This learning video presents an introduction to the
Flaws of Averages using three exciting examples: the “crossing of the
river” example, the “cookie” example, and the “dance class” example.
Averages are often worthwhile representations of a set of data by a
single descriptive number. The objective of this module, however, is to
simply point out a few pitfalls that could arise if one is not attentive
to details when calculating and interpreting averages." Aligns
with ID-A.2.
National Library of Virtual Manipulatives:
Box
Plots and Histograms
(Java required).
Use with ID-A.1.
National Center for Education Statistics:
Create a graph
Ohio Resource Center on YouTube:
Tutorials for High School Mathematics. Select the following:
OnlineStatBook:
Graphing Distributions is a chapter that addresses stem and leaf
displays, histograms, frequency polygons, box plots, dot plots, bar
charts, line graphs, and more. Exercises are included. The
project to develop the book was led by David Lane at Rice University.
PhET Interactive Simulations:
Plinko Probability. Per its description: "Drop balls through a triangular grid of pegs and
see them accumulate in containers. Switch to a histogram view and compare the
distribution of balls to an ideal binomial distribution. Adjust the binary probability
and develop your knowledge of statistics!" Aligns with ID-A.1, ID-A.2,
and IC-A.2.
Purple Math:
Shodor Interactivate:
Statistics and Probability: Interpreting Categorical and Quantitative Data:
Summarize, represent, and interpret data on a single count or
measurement variable. A series of nine lessons and 14 activities with virtual manipulatives
to investigate concepts such as box plots, histograms, stem-and-leaf
plots, measures of center and spread, the Bell curve, univariate and
bivariate data, normal distributions, skewed distributions. Aligns
with ID-A.
Stat Trek: Tutorials:
Statistics Canada: Statistics, Power from Data:
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Jay Hill:
Introduction to Descriptive Statistics--mean, median, mode,
central tendency, variation, range, variance, and standard deviation, simply explained.
U.S. Census Bureau:
- Commuting to Work: Box Plots, Central Tendency, and Outliers. Per
its description: "Students will calculate various measures of central
tendency using data on the number of people who bike to work in select
states. Students will then create a box plot to represent the data set
and answer conceptual questions about the impact of the data set’s
outlier."
Aligns with ID-A.1, ID-A.3, and math practice standards MP2 (reason
abstractly and quantitavely), MP4 (model
with math) and MP6 (attend to precision).
-
Describing and Comparing Data Distributions. Per its
description: "Students will use data on the organization, spending, and
populations of governments at different levels (city or town, county,
and state) to compare and contrast the distributions of these variables
in graphs, analyzing the shape, center, and spread of each."
Aligns with ID-A.2, ID-A.3, and math practice standards MP2
(reason abstractly and quantitavely) and MP6 (attend to
precision).
-
Over the Hill: Aging on a Normal Curve. Per its
description: "Students will use census data from a sample of 136
U.S. counties and other sample data to make estimates about the
U.S. population that is 65 or older in all other counties and
about other variables, using normal distribution models."
Aligns with ID-A.4 and math practice standard MP2 (reason
abstractly and quantitavely).
Teaching Channel Video:
Statistical Analysis to Rank Baseball Players: This video's
lesson objective: Rank the greatest NY Yankee homerun hitters using
statistical analysis. Questions for learners to consider are
included. Use to address ID-A.1, ID-A.2, and ID-A.3.
Online
Statistics Calculators: There are five calculators available
for measures of central tendency and dispersion, box and whisker plots,
linear regression, correlation coefficients, and scatter-plots. Aligns
with ID-A.1 and ID-A.2.
Wolfram Demonstrations Project:
Download the free Wolfram CDF player
to interact with the following manipulatives. Note: Within the
Wolfram Demonstration Project are
14 manipulatives addressing ID-A.1,
5 manipulatives for ID-A.2,
9 manipulatives for ID-A.3,
12 manipulatives for
ID-A.4. Among those:
-
Stylized pie and bar charts for fast food nutrition:
Illustrates styling options. Aligns with ID-A.1.
-
Exploring skewness in box plots: Aligns with ID-A.1.
-
Bin width and histogram
shape: This histogram presents data regarding the time between
eruptions of Old Faithful in Yellowstone. Aligns with
ID-A.1.
-
Line plots, histograms, and stem-and-leaf plots: Various
ways to display data. Aligns with ID-A.1, ID-A.2.
-
Descriptions of univariate data: Aligns with ID-A.2.
-
Mean, median, mode: Aligns with ID-A.2.
-
Mean, median, and standard deviation for random values:
Aligns with ID-A.2.
-
The 2001 CSO Mortality Tables: The 2001 CSO Mortality Tables represent the most
widely used approximations as to the expected rates of death in the United
States as a function of age. The demonstration manipulates
the data to show three types of plots. Aligns with ID-A.1,
ID-A.3, MD-A.4, MD-B.6.
-
Area of a normal distribution: Aligns with ID-A.4.
-
Matching temperature data to a normal distribution: Aligns with ID-A.4.
-
Standard normal distribution areas: Aligns with ID-A.4.
-
Impact of sample size on approximating the normal distribution: Aligns with ID-A.4.
-
Bell
curves: Aligns with ID-A.4.
-
Mean and standard deviation of a distribution: Aligns with ID-A.4.
YouTube video: GCSE Maths Median
and IQR: This short video shows how to find a median, lower
quartile, upper quartile, then inter-quartile range.
Multiple Choice:
MathBitsNotebook: Algebra 1:
Statistics: Data Distributions includes lessons, then practice
problems on categorizing data, box plots, outliers, measures of center
and shapes of distributions, standard deviation, and interpreting
graphs. Use with ID-A.1, ID-A.2, and ID-A.3.
MathsIsFun.com:
-
Quartiles: How to calculate quartiles and interquartile range
and their association to a box and whisker plot. Following the
explanation are ten multiple choice exercises. Use with ID-A.1 and
ID-A.2.
- Outliers:
Contains a concise explanation of the role outliers play in data
analysis involving mean, median, and mode. Following the
explanation are eight multiple choice exercises. Use with ID-A.3.
-
Standard deviation and variance: After explanation and
examples, there are 10 multiple choice exercises. Use with
ID-A.4.
-
Normal Distribution: Contains a concise explanation of the
normal distributions, standard deviation (how to compute it, and
accompanied by a standard deviation calculator), and z-scores with
visuals and worked examples. Following the explanation are ten
multiple choice exercises. Use with ID-A.4.
-
Standard Normal Distribution Table: includes a manipulative to
work with z-scores on a normal distribution and a table of values associated with percent of
population with worked example. Following the explanation are
ten multiple choice exercises. Use with ID-A.4.
Constructed-response:
AlgebraLab.org:
Mean, Median, Mode. Lesson, interactive online practice problems.
Show the Related AlgebraLab documents for activities, additional practice
problems and word problems. Aligns with ID-A.2.
Khan Academy: HSS-S-ID
includes HSS-ID.A.1 through HSS-ID.A.4 multiple choice and
constructed-response Common Core aligned problems.
Also see the
Analyzing Categorical Data unit with practice questions with videos.
Statistics: Power from Data:
- Ch. 9:
Graph Types: Explanations of graph types. A tool is presented for learners to
create graphs. Practice exercises are included.
- Ch. 11:
Measures of
Central Tendency: Explanations on mean, median, mode with exercise problems and answers.
- Ch. 12:
Measures of Spread:
Explanations on range and quartiles, variance and standard deviation,
box and whisker plots with exercise problems and answers.
Zweigmedia.com: Tutorials and examples using fill-in or
multiple choice to test understanding. Learners can also choose to
do game versions of some topics. Use with ID-A:
Performance tasks:
Illustrative Mathematics:
Statistics and
Probability:
Mathematics Assessment Project:
Standards: High School: Statistics & Probability:
Mathematics Vision Project,
Secondary 1 Student Edition:
-
Module
8: Modeling Data: This module contains 8 classroom tasks. Module 7 addresses
standards ID-A.1, ID-A.2, ID-A.3 and ID-B.5, ID-B.6 and ID-C.7, ID-C.8.
Task 1: Texting by the Numbers; and Task 2: Data Distributions align to
standards ID-A.1, ID-A.2, and ID-A.3.
Mathematics Vision Project,
Secondary
3 Student Edition:
NCTM's Reasoning and Sense Making Task Library: Eruptions: Old Faithful includes the task overview, teacher notes for its use, and student activity sheet. Aligns with IC-A.1,
ID-A.1, and mathematical practice standards 1, 3, and 5.
Statistics in Schools from the U.S. Census Bureau:
Activities:
Math: 9-12:
-
Commuting to Work: Box Plots, Central Tendency, Outliers.
Students "calculate various measures of central tendency using
data on the number of people who bike to work in select states.
Students will then create a box plot to represent the data set
and answer conceptual questions about the impact of the data
set’s outlier." Aligns with ID-A.1.
-
Differences in Earnings Across Sex and Educational
Attainment: Comparing Box Plots. Students "interpret box
plots that represent the national median earnings of men and
women aged 25 and older whose highest levels of educational
attainment are either a high school diploma (or equivalent) or a
bachelor’s degree. Students will use the box plots to identify
each data set’s median, maximum, minimum, first quartile, third
quartile, range, interquartile range, and outliers. They will
also compare the box plots to draw conclusions about differences
in earnings between the sexes and between levels of educational
attainment." Aligns with ID-A.1, ID-A.2, ID-A.3.
-
Describing and Comparing Data Distributions. Students
"use data on the organization, spending, and populations of
governments at different levels (city or town, county, and
state) to compare and contrast the distributions of these
variables in graphs [box plots and histograms], analyzing the
shape, center, and spread of each." Aligns with
ID-A.2, ID-A.3.
-
Census in Countries: Describing and Comparing Histograms to
Understand American Life. Students "analyze
a variety of county-level census data, including on employment,
technology, and transportation, in histograms to compare and
contrast the shapes of their distributions and to interpret
measures of center and spread in context." Aligns with ID-A.2, ID-A.3.
-
The New Normal. Students "explore
distributions of various census data sets to determine whether
it can be reasonably assumed that those data follow a normal
distribution, based on students’ analysis of either a histogram
or a normal probability plot for each data set. They will then
discuss their findings with a partner who analyzed the other
type of graph for each data set." Aligns with ID-A.3.
-
Over the Hill: Aging on a Normal Curve. Students "use
census data from a sample of 136 U.S. counties and other sample
data to make estimates about the U.S. population that is 65 or
older in all other counties and about other variables, using
normal distribution models." Aligns with ID-A.4.
Back to top
ID-B: Summarize, represent, and interpret data on two categorical
and quantitative variables
Standards:
- ID-B.5. Summarize categorical data for two
categories in two-way frequency tables. Interpret relative
frequencies in the context of the data (including joint, marginal,
and conditional relative frequencies). Recognize possible
associations and trends in the data.
- ID-B.6. Represent data on two quantitative
variables on a scatter plot, and describe how the variables are
related.
- ID-B.6.a. Fit a function to the data;
use functions fitted to data to solve problems in the context of
the data. Use given functions or choose a function suggested by
the context. Emphasize linear, quadratic, and exponential models.
- ID-B.6.b. Informally assess the fit of a
function by plotting and analyzing residuals.
- ID-B.6.c. Fit a linear function for a
scatter plot that suggests a linear association.
Notes:
Each type of graph has its advantages and disadvantages.
Line graphs and histograms are only used with continuous data, which means
that theoretically all values are possible (no gaps) in an interval
(between any two it is possible to get another). Examples include height,
weight, time to complete your homework, and time to complete a trip. Line
graphs are good to demonstrate trends, such as sales in a company over time or
changes in temperature over time.
Bar graphs and circle graphs (often called pie charts) are only used with discrete data,
which means that only certain values (gaps) are possible.
Examples typically include counting, as in the number of students in a class,
the number of crimes reported to the police, or the number of tickets sold to a
game. Note that pie charts are good for presenting percentages. Bar
graphs can be presented vertically or horizontally. For example, a
horizontal bar graph could be used to compare expenses among four departments of
a company.
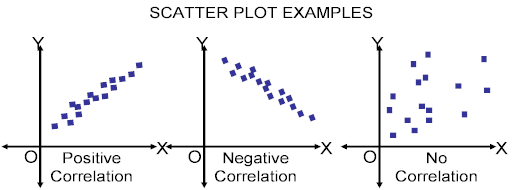
Scatter plots are used for experimental data to determine if there is a
relationship between the variables studied.
When creating graphs, note the following 10 common errors, provided by
CanTeach (CA):
- No title on graph
- Source of data not given
- Pictograph - no key
- Scales are interrupted
- Scales are not labeled
- Symbols in pictographs not same size or equally spaced on graph
- Use of 2 or 3 dimensional objects to compare data (area/volume)
- Scales do not start at zero
- Numbers on axis (vertical or horizontal) not equally spaced
- Scale is selected to produce desired result
Technology-enhanced investigations:
Alcula.com:
CK-12: Algebra: Concepts, video, and practice problems for learners.
College Preparatory Math: Student Tutorials:
TI-84
Graphing Calculator: Bivariate Data: Videos and screen shots
illustrating use of the calculator for setting up a scatter plot,
non-linear regressions, least squares regression line, the
correlation coefficient, residuals & residual plots.
Imagine Learning Classroom (formerly LearnZillion) subscription
needed:
- Lesson set:
Summarize categorical data for two categories in two-way
frequency tables, interpret relative frequencies, and recognize
trends: Three video lessons: Interpret a two-way frequency
table, compute conditional relative frequencies, determine
associations by comparing conditional relative frequencies.
Aligns with ID-B.5.
- Lesson set (additional):
Summarize categorical data for two categories in two-way
frequency tables, interpret relative frequencies, and recognize
trends: Three additional video lessons: Set up a two-way frequency
table, use two-way frequency tables by determining if the data
is a frequency count or a relative frequency, calculate
probabilities by using the data in a two-way frequency table.
Aligns with ID-B.5.
- Lesson set:
Represent and describe data on two quantitative variables on a
scatter plot: video lessons: Describe the relationship
between two quantitative variables by looking at a scatter plot,
describe a relationship in terms of strength and direction, make
predictions using a line of best fit, draw and calculate
residuals, understand the least squares regression line and find
its equation using technology. Aligns with ID-B.6.
MIT BLOSSOMS: Video lesson with additional teacher and learner
resources. Description is from the video summary. Flu Math Games:
"This video lesson shows students that math can play a role in
understanding how an infectious disease spreads and how it can
be controlled." Additional simulations are included.
Aligns with Algebra standards SSE-B.3.c and REI-A.1; Function
standards IF-C.8.b, BF-B.4.a, and LE-A-1.(a, c); and Statistics
and Probability standards ID-B.6.a, IC-A.1, IC-B.4, CP-A.2, and MD-A.1.
National Library of Virtual Manipulatives:
Scatterplots (Java required).
NCTM Illuminations:
Ohio Resource Center on YouTube: Tutorials for High School Mathematics:
Lines of Fit:
Defining and finding lines of fit using real data.
PhET Interactive Simulations:
Saltire Software: Common Core Nuggets: There are five applets addressing
residual plots and least squares, which align with ID-B.6.
Shodor Interactivate:
-
Linear Regression and Correlation: Lesson introducing
correlations between two variables and line of best fit.
-
Univariate and Bivariate Data: Lesson introducing the
difference between these two types and how to determine the best
graph to use to display the data.
-
Regression: A virtual manipulative to plot a bivariate data
set, determine the line of best fit for the data, and then check
the accuracy of a line of best fit.
Stat-Trek: Tutorials:
U.S. Census Bureau:
Applying
Correlation Coefficients - Educational Attainment and Unemployment. Per
its description: "Students will use state and regional unemployment data
for various education levels to create scatter plots and calculate
correlation coefficients [using technology and by hand]. Students will then
compare scatter plots with different strengths of linear relationships and will
determine the impact of any influential points on the correlation coefficient."
Aligns with ID-B.6, ID-C.8, and math practice standards MP4 (model
with math) and MP6 (attend to precision).
Wolfram Demonstrations Project:
Download the free Wolfram CDF player
to interact with the following manipulatives. Note: Within the
Wolfram Demonstration Project are
1 manipulative addressing ID-B.5,
20 manipulatives for ID-B.6. Among those:
Multiple Choice:
MathsIsFun.com:
Scatter Plots: Contains a concise explanation of the scatter
plot and its relation to line of fit and correlation. Following the
explanation are nine multiple choice exercises. Use with ID-B.6.
Khan Academy:
Exploring Bivariate Numerical Data unit. Practice questions with videos.
MathBitsNotebook: Algebra 1:
Statistics: Bivariate Data includes lessons, then practice
problems on two-way frequency tables, fitting functions to data,
residuals, linear regression, correlation and correlation
coefficients, slopes and intercepts of linear models. Use with
ID-B.5, ID-B.6, ID-C.7, ID-C.8, and ID-C.9.
Constructed-response:
Khan Academy:
HSS-S-ID
includes HSS-ID.B.5 and HSS-ID.B.6 multiple choice and
constructed-response Common Core aligned problems.
Also see the
Summarizing quantitative data unit with practice questions with videos.
The Math
You Need, When You Need It: Constructing a line of best fit includes
tutorials followed by practice problems focusing on real-life scenarios
on this topic that geoscientists would encounter. The site is by
SERC, the Science Education Resource Center at Carleton College.
Zweigmedia.com: Tutorials and examples using fill-in to test understanding. Learners can also choose to
do game versions of some topics. Use with ID-B.6:
Linear regression
Performance tasks:
Illustrative Mathematics:
Statistics and
Probability:
Inside Mathematics: MARS Tasks: The following align with ID-B.6:
-
Population:
Students work with a scatter plot to identify specific information
on it, describe main features of a scatter plot and make sense of
trends in order to graph a line to represent average density and
calculate density relationships in the given situation.
-
Snakes:
Students work with two scatter plots to make sense of data
displayed. They make sense of a table and look for trends including
correlations and lines of best fit, and they make inferences based
on data and conclusions about a situation being modeled.
Mathematics Assessment Project:
Standards: High School: Statistics & Probability:
Mathematics Vision Project,
Secondary 1 Student Edition:
Module
8: Modeling Data: This module contains eight classroom tasks. Module 8 addresses
standards ID-A.1, ID-A.2, ID-A.3 and ID-B.5, ID-B.6 and ID-C.7, ID-C.8.
Task 3: After School Activity; and Task 4: Relative Frequency align to
standard ID-B.5. Task 7: Getting Schooled; and Task 8: Rocking the
Residuals align to standard ID-B.6.
Statistics in Schools from the U.S. Census Bureau:
Activities:
Math: 9-12:
- Linear Models –
Analyzing Relationships: Marriage, Divorce,
and Linear Regression. Students "create a scatter plot,
find a line of best fit, and analyze the relationship between
the two variables (i.e., sex and marriage/ divorce rates). They
will also use a residual plot, explain the meaning of the slope
and of the y-intercept of the line of best fit, and investigate
the effect of outliers on this line." Aligns with ID-B.6, ID-C.7.
-
Applying Correlation Coefficients: Educational Attainment
and Unemployment. Students "use state and regional unemployment data
for various education levels to create scatter plots and calculate correlation
coefficients. Students will then compare scatter plots with
different strengths of linear relationships and will determine
the impact of any influential points on the correlation coefficient.
Aligns with ID-B.6, ID-C.8.
Back to top
ID-C: Interpret linear models
Standards:
- ID-C.7. Interpret the slope (rate of
change) and the intercept (constant term) of a linear model in the
context of the data.
- ID-C.8. Compute (using technology) and
interpret the correlation coefficient of a linear fit.
- ID-C.9. Distinguish between correlation and causation.
Technology-enhanced investigations:
Khan Academy:
Imagine Learning Classroom (formerly LearnZillion) subscription
needed:
- Lesson set:
Interpret the slope and intercept of a linear function in
context: Three video lessons: Distinguish between
scatterplots and lines; interpret intercepts and slope using a
line of best fit. Aligns with ID-C.7.
- Lesson set:
Interpret the slope and the intercept of a linear model using
data: Four video lessons: Interpret the parts of a linear
model, find the slope of a linear function by using two points,
find the slope and y-intercept of a line by using the slope
formula and analyzing linear models, solve real-world problems
using slope and y-intercept, determine type of slope by
analyzing linear function word problems. Aligns with
ID-C.7.
- Lesson set:
Find correlation coefficient of a linear fit: Three video
lessons: Understand correlation in terms of the strength of a
relationship, find the correlation coefficient by using
technology, understand and interpret the slope of a regression
line. Aligns with ID-C.8.
- Lesson set:
Compute and interpret the correlation coefficient of a linear
fit: Four video lessons: Use the correlation coefficient to
assess the strength of a linear fit, assess the appropriateness
of a linear correlation model, calculate the correlation
coefficient by using a graphing calculator, solve problems using
linear regression. Aligns with ID-C.8.
- Lesson set:
Distinguish between correlation and causation: Three video
lessons: Understand causation; distinguishing correlation and
causation using the reverse causation example and by examining a
common causation example. Aligns with ID-C.9.
- Lesson set:
Distinguish between correlation and causation and assess
causation: Three video lessons: Differentiate between
correlation and causation, evaluate language that confuses
correlation and causation, establish causation through
experimental design. Aligns with ID-C.9.
PhET Interactive Simulations:
Least-Squares Regression. Aligns with ID-B.6, ID-B.6.a,
ID-B.6.b, ID-B.6.c, and ID-C.8.
Stat Trek: Tutorial:
Linear Correlation Coefficient: The tutorial includes a video,
and explanation on how to interpret and calculate the correlation
coefficient. Use with ID-C.8.
Social Science Statistics:
Pearson
Correlation Coefficient Calculator. Free online
calculator. Use with ID-C.8.
College Preparatory Math: Student Tutorials:
TI-84
Graphing Calculator: Bivariate Data: Videos and screen shots
illustrating use of the calculator for setting up a scatter plot,
non-linear regressions, least squares regression line, the
correlation coefficient, residuals & residual plots.
U.S. Census Bureau:
Applying
Correlation Coefficients - Educational Attainment and Unemployment. Per
its description: "Students will use state and regional unemployment data
for various education levels to create scatter plots and calculate
correlation coefficients [using technology and by hand]. Students will then
compare scatter plots with different strengths of linear relationships and will
determine the impact of any influential points on the correlation coefficient."
Aligns with ID-B.6, ID-C.8, and math practice standards MP4 (model
with math) and MP6 (attend to precision).
Wolfram Alpha: Wolfram Demonstrations Project:
Download the free Wolfram CDF player
to interact with the following manipulatives. Note: Within the
Wolfram Demonstration Project are
3 manipulatives for ID-C.8. Among those:
-
Correlation and regression explorer: Aligns with ID-B.6, ID-C.8.
- Anscombe
Quartet: The Anscombe Quartet is comprised of four scatterplots that have
nearly identical correlations, as well as means and standard
deviations, but disparate shapes. These graphs show the crucial
role that data visualization plays in developing a sensible
statistical model. Aligns with ID-C.8.
Multiple Choice:
Khan Academy:
HSS-S-ID
includes HSS-ID.C.7 through HSS-ID.C.9 Common Core aligned problems.
Also see the
Exploring Bivariate Numerical Data unit with practice questions with videos.
MathBitsNotebook: Algebra 1:
Statistics: Bivariate Data includes lessons, then practice problems
on two-way frequency tables, fitting functions to data, residuals,
linear regression, correlation and correlation coefficients, slopes and
intercepts of linear models. Use with ID-B.5, ID-B.6, ID-C.7,
ID-C.8, and ID-C.9.
MathsIsFun.com:
Correlation:
Contains a concise explanation of the meaning of correlation,
correlation does not mean causation, and how to calculate the
correlation coefficient. Worked examples are provided.
Following the explanation are four multiple choice exercises. Use with
ID-C.8 and ID-C.9.
Constructed-response:
Performance tasks:
Illustrative Mathematics:
Statistics and
Probability:
Mathematics Assessment Project:
Standards: High School: Statistics & Probability:
Task 217:
Interpreting Statistics: A Case of Muddying the Waters
Mathematics Vision Project,
Secondary 1 Student Edition:
Module
8: Modeling Data: This module contains eight classroom tasks.
Module 8 addresses standards ID-A.1, ID-A.2, ID-A.3 and ID-B.5, ID-B.6
and ID-C.7, ID-C.8. Task 5: Connect the Dots aligns to standard
ID-C.8. Task 6: Making More $; and Task 7: Getting Schooled align to
both standards ID-C.7, ID-C.8.
Statistics in Schools from the U.S. Census Bureau:
Activities:
Math: 9-12:
- Linear Models –
Analyzing Relationships: Marriage, Divorce,
and Linear Regression. Students "create a scatter plot,
find a line of best fit, and analyze the relationship between
the two variables (i.e., sex and marriage/ divorce rates). They
will also use a residual plot, explain the meaning of the slope
and of the y-intercept of the line of best fit, and investigate
the effect of outliers on this line." Aligns with ID-B.6, ID-C.7.
- Applying Correlation Coefficients: Educational Attainment
and Unemployment. Students "use state and regional unemployment data
for various education levels to create scatter plots and calculate correlation
coefficients. Students will then compare scatter plots with
different strengths of linear relationships and will determine
the impact of any influential points on the correlation coefficient.
Aligns with ID-B.6, ID-C.8.
- Educational Attainment and Marriage: Testing a Correlation
Coefficient's Significance. Students "develop,
justify, and evaluate conjectures about the relationship between
two quantitative variables over time in the United States: the
median age (in years) when women first marry and the percentage
of women aged 25–34 with a bachelor’s degree or higher. Students
will write a regression equation for the data, interpret in
context the linear model’s slope and y-intercept, and find the
correlation coefficient (r), assessing the strength of the
linear relationship and whether a significant relationship
exists between the variables. Students will then summarize their
conclusions and consider whether correlation implies causation."
Aligns with ID-C.8, ID-C.9, and IC-A.1.
Related to the above task is the article: What
Is The Aim Of Finding Correlation? Why Is It Used If Correlation
Doesn’t Imply Causation? posted at ScienceABC. Author Argha Sengupta (2022,
July 8) delved into Finding Meaning From Random Data: Exploratory
Analysis and Correlation May Not Imply Causation, the latter of which
might be owing to an influence of a third variable.
Back to top
Common Core Math:
Intro | HS Statistics & Probability Domain:
ID | IC | CP | MD |

![]()

![]()

![]()